|
This document is under active development!
If you find errors or omissions in this document, please don’t hesitate to {uri-conrad-mail}[send me a mail]. |
This journal assumes you are comfortable with a linux environment as most of the published work here uses an Ubuntu distribution as the work station.
Introduction
This journal was started in order to document my exploration of OpenWrt through the prpl foundation.
Building OpenWrt
3. Dependencies
The following is a list of packages that have to be installed in the system. Each package has a brief description taken with the help of apt-cache:
-
build-essential : Informational list of build-essential packages. If you do not plan to build Debian packages, you don’t need this package. Starting with dpkg (>= 1.14.18) this package is required for building Debian packages. This package contains an informational list of packages which are considered essential for building Debian packages. This package also depends on the packages on that list, to make it easy to have the build-essential packages installed.
-
subversion : Apache Subversion, also known as svn, is a centralised version control system. Version control systems allow many individuals (who may be distributed geographically) to collaborate on a set of files (source code, websites, etc). Subversion began with a CVS paradigm and supports all the major features of CVS, but has evolved to support many features that CVS users often wish they had.
-
libncurses5-dev : The ncurses library routines are a terminal-independent method of updating character screens with reasonable optimization.This package contains the header files, static libraries and symbolic links that developers using ncurses will need.
-
zlib1g-dev : Zlib compression library for development. zlib is a library implementing the deflate compression method found in gzip and PKZIP. This package includes the development support files.
-
gawk : GNU awk, a pattern scanning and processing language `awk', a program that you can use to select particular records in a file and perform operations upon them.
-
gcc-multilib : GNU C compiler (multilib files). This is the GNU C compiler, a fairly portable optimizing compiler for C.
-
flex : A fast lexical analyzer generator. Flex is a tool for generating scanners: programs which recognized lexical patterns in text.
-
git-core : A fast, scalable, distributed revision control system. Git is popular version control system designed to handle very large projects with speed and efficiency; it is used for many high profile open source projects, most notably the Linux kernel.
-
gettext : GNU Internationalization utilities. Interesting for authors or maintainers of other packages or programs which they want to see internationalized.
-
qemu-system-mips : QEMU full system emulation binaries (mips) QEMU is a fast processor emulator: currently the package supports MIPS emulation. By using dynamic translation it achieves reasonable speed while being easy to port on new host CPUs.
3.1. Installing Dependencies
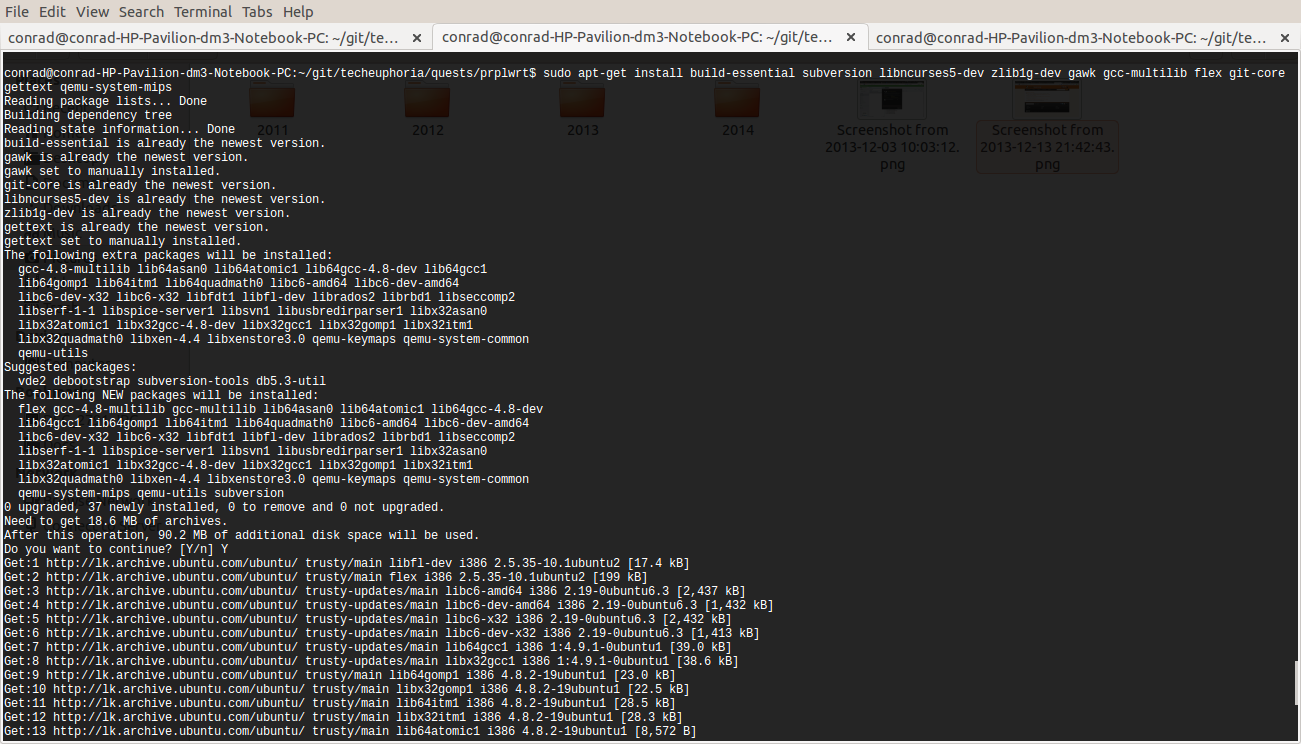
To install the dependencies we use the apt-get command line application in a terminal. The dependencies are installed as shown below.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~$ sudo apt-get install build-essential subversion libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk gcc-multilib flex git-core gettext qemu-system-mipsThe use of sudo is required to grant root priveledges to the apt-get command while executing as changes will be made in the system directories. If you don’t have sudo access talk to your system administrator. Getting sudo access is a matter of editing the /etc/sudoers file. For further information I suggest you read about RootSudo in the Ubuntu community pages.
3.2. Problems With Installation
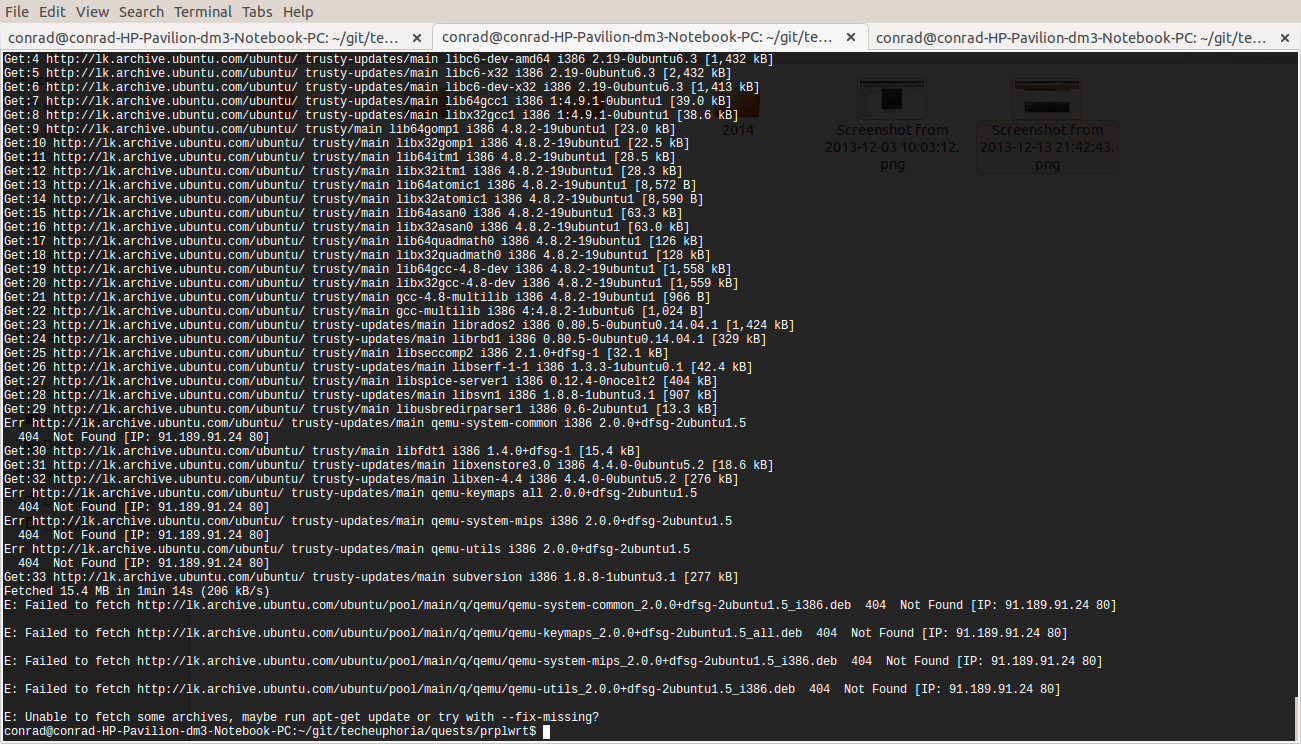
While installing the above packages in my work station I encountered the following errors which stopped the installation process
Err http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main qemu-system-common i386 2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
Err http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main qemu-keymaps all 2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
Err http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main qemu-system-mips i386 2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
Err http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ trusty-updates/main qemu-utils i386 2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
E: Failed to fetch http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/q/qemu/qemu-system-common_2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5_i386.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
E: Failed to fetch http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/q/qemu/qemu-keymaps_2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5_all.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
E: Failed to fetch http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/q/qemu/qemu-system-mips_2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5_i386.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
E: Failed to fetch http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/q/qemu/qemu-utils_2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.5_i386.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
E: Unable to fetch some archives, maybe run apt-get update or try with --fix-missing? (1)| 1 | Two recommendations provided by apt-get i.e. doing a system update OR passing a --fix-missing option to the command. |
3.3. Solving The Installation Errors
In my case the first option of doing a system update helped. So the actual steps that worker for my workstation are listed in the snippet below:
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/techeuphoria/quests/prplwrt$ sudo apt-get update (1)
Ign http://dl.google.com stable InRelease
Get:1 http://dl.google.com stable Release.gpg [198 B]
Ign http://extras.ubuntu.com trusty InRelease
.
.
.
Ign http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com trusty/multiverse Translation-en_US
Ign http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com trusty/restricted Translation-en_US
Ign http://lk.archive.ubuntu.com trusty/universe Translation-en_US
Fetched 1,722 kB in 19s (87.8 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Dones (2)
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/techeuphoria/quests/prplwrt$ sudo apt-get install build-essential subversion libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk gcc-multilib flex git-core gettext qemu-system-mips (3)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
.
.
.
etting up qemu-keymaps (2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.6) ...
Setting up qemu-system-mips (2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.6) ...
Setting up qemu-utils (2.0.0+dfsg-2ubuntu1.6) ...
Setting up subversion (1.8.8-1ubuntu3.1) ...
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.19-0ubuntu6.3) ... (4)
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/techeuphoria/quests/prplwrt$| 1 | Do an update with sudo apt-get update |
| 2 | sudo apt-get update succeeds with no errors |
| 3 | Do an install with sudo apt-get install … |
| 4 | sudo apt-get install succeeds with not errors |
4. Cloning The OpenWrt GIT Repository
Now that we have all the dependencies installed in the system it is time to clone the repository. The OpenWrt project is maintained using GIT. So change directory to the location where you would like to keep the source code and clone the repository as follows:
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git$ git clone git://git.openwrt.org/openwrt.git (1)
Cloning into 'openwrt'...
remote: Counting objects: 287173, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (83724/83724), done.
remote: Total 287173 (delta 195562), reused 281130 (delta 190331)
Receiving objects: 100% (287173/287173), 106.03 MiB | 163.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (195562/195562), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
Checking out files: 100% (7375/7375), done. (2)
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git$| 1 | Command to clone the git repository at git://git.openwrt.org/openwrt.git |
| 2 | Clone completes without any errors |
5. Update OpenWrt Packages
Before we proceed to build the image for OpenWrt we have to run a package update script which updates software that can be included in the OpenWrt image.
The script checks the feed.conf.default file to get a list of all the necessary packages to be updated
5.1. Break Up Of Update Process
The snippet below captures the steps that take place in order to update the OpenWrt packages:
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git$ cd openwrt/
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$ ls
BSDmakefile config Config.in docs feeds.conf.default include LICENSE Makefile package README rules.mk scripts target toolchain tools (1)
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$ ./scripts/feeds update -a (2)
Updating feed 'packages' from 'https://github.com/openwrt/packages.git' ... (3)
Cloning into './feeds/packages'...
remote: Counting objects: 1852, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (1535/1535), done.
remote: Total 1852 (delta 82), reused 1479 (delta 67)
Receiving objects: 100% (1852/1852), 2.10 MiB | 388.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (82/82), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
Create index file './feeds/packages.index'
Collecting package info: done
Updating feed 'luci' from 'https://github.com/openwrt/luci.git' ... (4)
Cloning into './feeds/luci'...
remote: Counting objects: 3325, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2181/2181), done.
remote: Total 3325 (delta 951), reused 2585 (delta 566)
Receiving objects: 100% (3325/3325), 3.72 MiB | 272.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (951/951), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
Create index file './feeds/luci.index'
Collecting package info: done
Updating feed 'routing' from 'https://github.com/openwrt-routing/packages.git' ... (5)
Cloning into './feeds/routing'...
remote: Counting objects: 248, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (201/201), done.
remote: Total 248 (delta 15), reused 180 (delta 12)
Receiving objects: 100% (248/248), 184.90 KiB | 95.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (15/15), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
Create index file './feeds/routing.index'
Collecting package info: done
Updating feed 'telephony' from 'http://git.openwrt.org/feed/telephony.git' ... (6)
Cloning into './feeds/telephony'...
remote: Counting objects: 187, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (164/164), done.
remote: Total 187 (delta 25), reused 45 (delta 3)
Receiving objects: 100% (187/187), 97.49 KiB | 94.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (25/25), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
Create index file './feeds/telephony.index'
Collecting package info: done
Updating feed 'management' from 'https://github.com/openwrt-management/packages.git' ... (7)
Cloning into './feeds/management'...
remote: Counting objects: 29, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (19/19), done.
remote: Total 29 (delta 3), reused 22 (delta 2)
Unpacking objects: 100% (29/29), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
Create index file './feeds/management.index'
Collecting package info: done| 1 | Contents of the OpenWrt directory |
| 2 | Script to update the packages of OpenWrt |
| 3 | Updating packages packages from https://github.com/openwrt/packages.git |
| 4 | Updating luci from https://github.com/openwrt/luci.git |
| 5 | Updating routing from https://github.com/openwrt-routing/packages.git |
| 6 | Updating telephony from http://git.openwrt.org/feed/telephony.git |
| 7 | Updating management from https://github.com/openwrt-management/packages.git |
6. Configuring The System Image
Before we can build the image that is booted up by our hardware or emulator we need to configure the build for the right target system and also with the correct features that are required by the system when it runs. The image is the Linux kernel along with a minimal file system which contains the binary applications and libraries which will be essential for the applications running on the system.
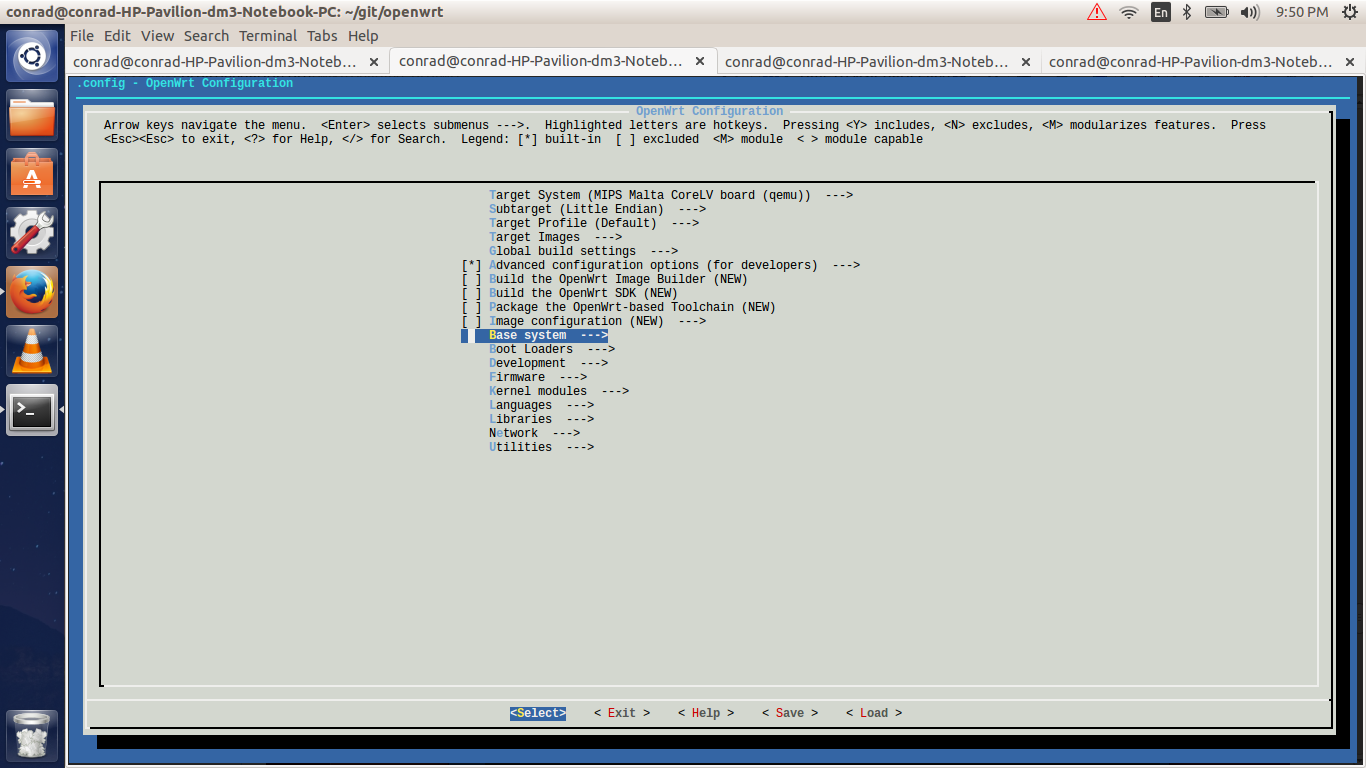
The configuration process is similar to that of the Linxu kernel where we run make menuconfig. The sections below will describe our various selections along with appropriate screen shots and placeholders for the various options. Additional features can be configured based on the requirements for the system.
6.1. Make Menuconfig
If you’ve installed the dependencies given above you should have no problem running the make menuconfig command. The execution of the make menuconfig should be done in the OpenWrt directory.
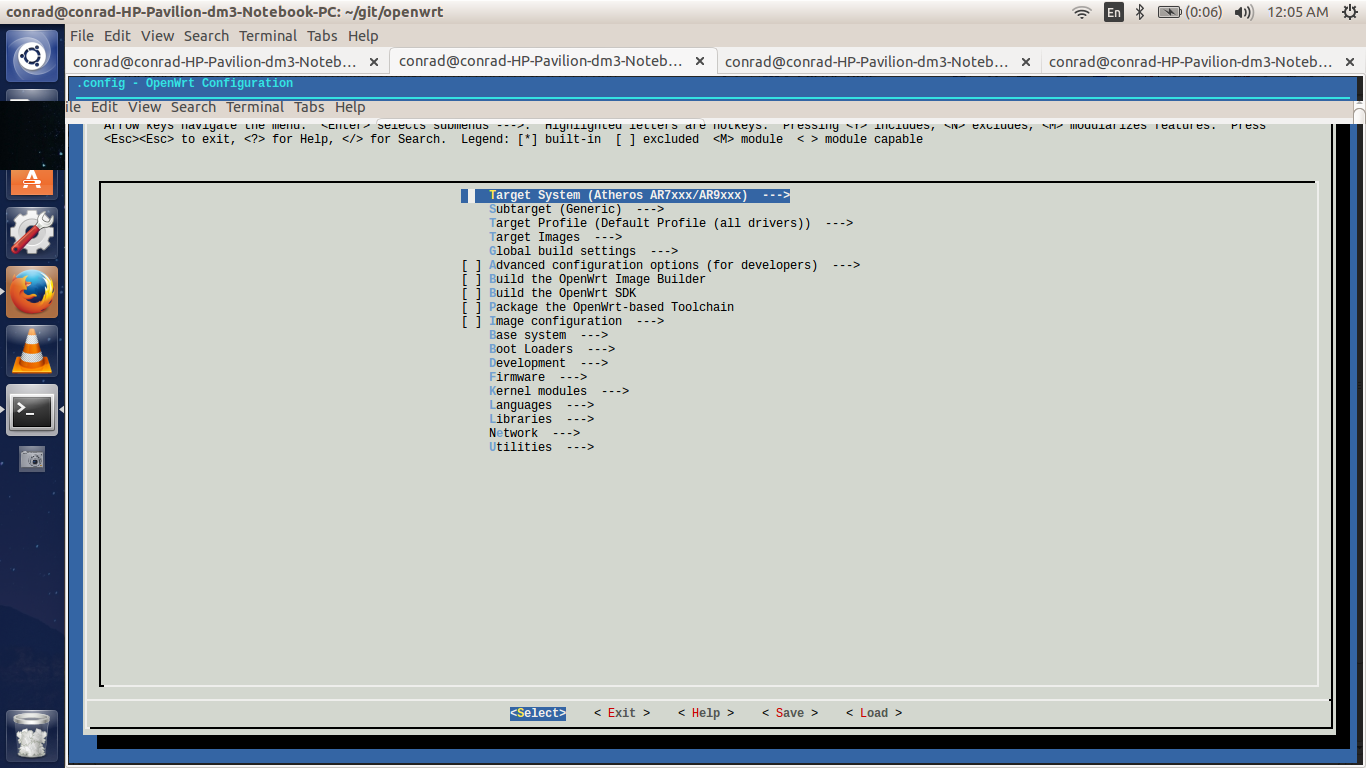
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$ make menuconfigOn running make menuconfig in the OpenWrt directory you should see a screen as shown below:
6.2. Selecting The Target System
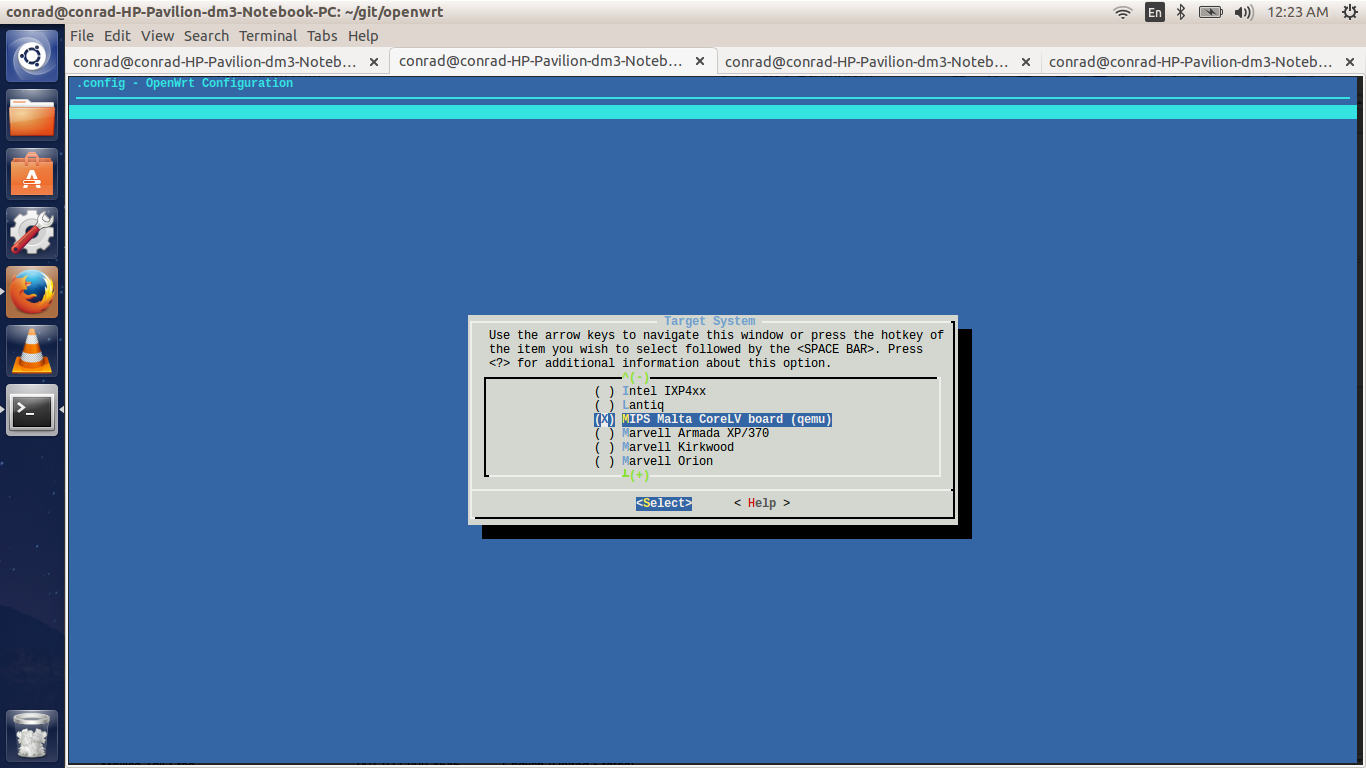
The first screen of the make menuconfig command shows the cursor highlighting the Target System. The target system selected is Atheros AR7xxx/AR9xxx. To change the selection hit the enter key. There will be other targets present. In our case we plan to run our built image on an emulator i.e. qemu for the MIPS Malta CoreLV board. Navigate the list of target options available using the UP and DOWN arrow keys until the "MIPS Malta CoreLV board (qemu)" is selected
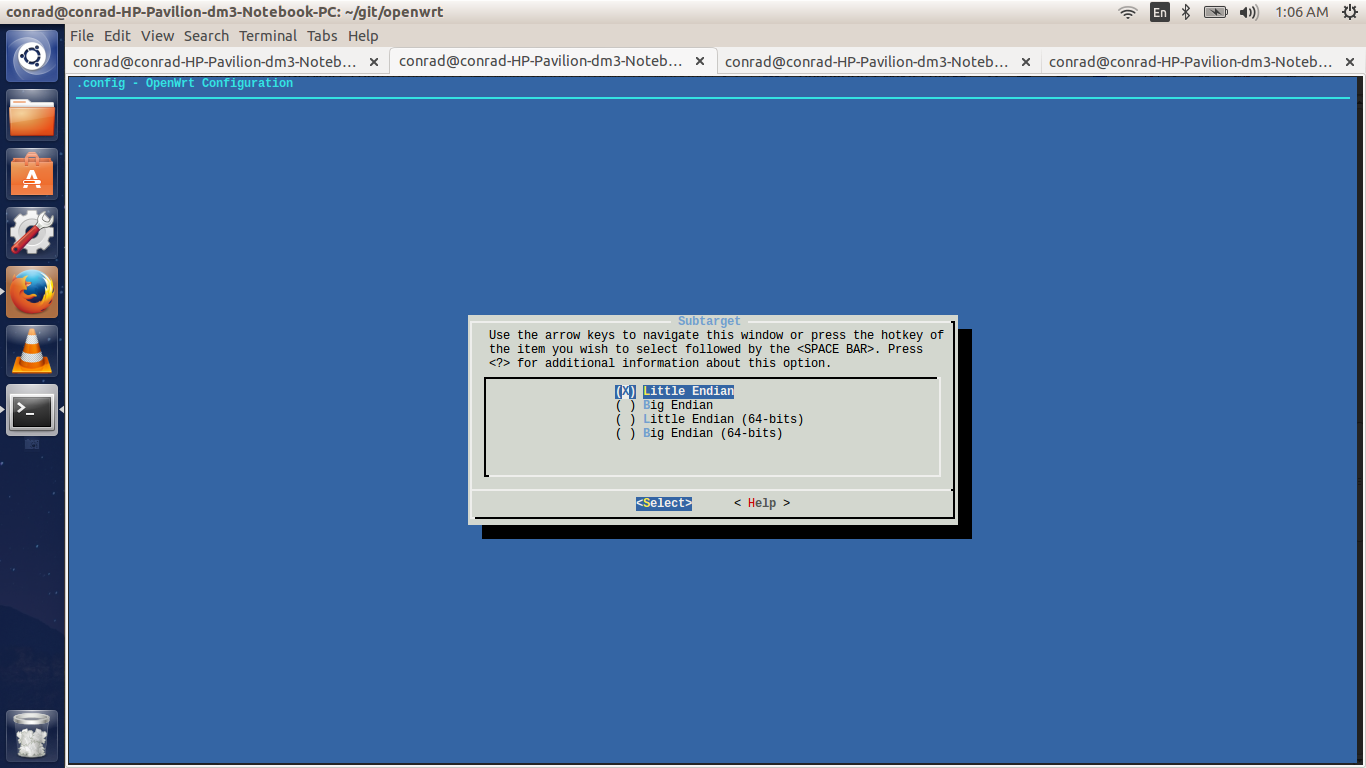
6.3. Selecting The Subtarget System
If your target selected has further subtargets then you will have to chose an appropriate subtarget. The four subtargets available for MIPS Malta CoreLV (qemu) are:
-
Little Endian
-
Big Endian
-
Little Endian(64 bit)
-
Big Endian(64 bit)
We keep the default i.e. Little Endian
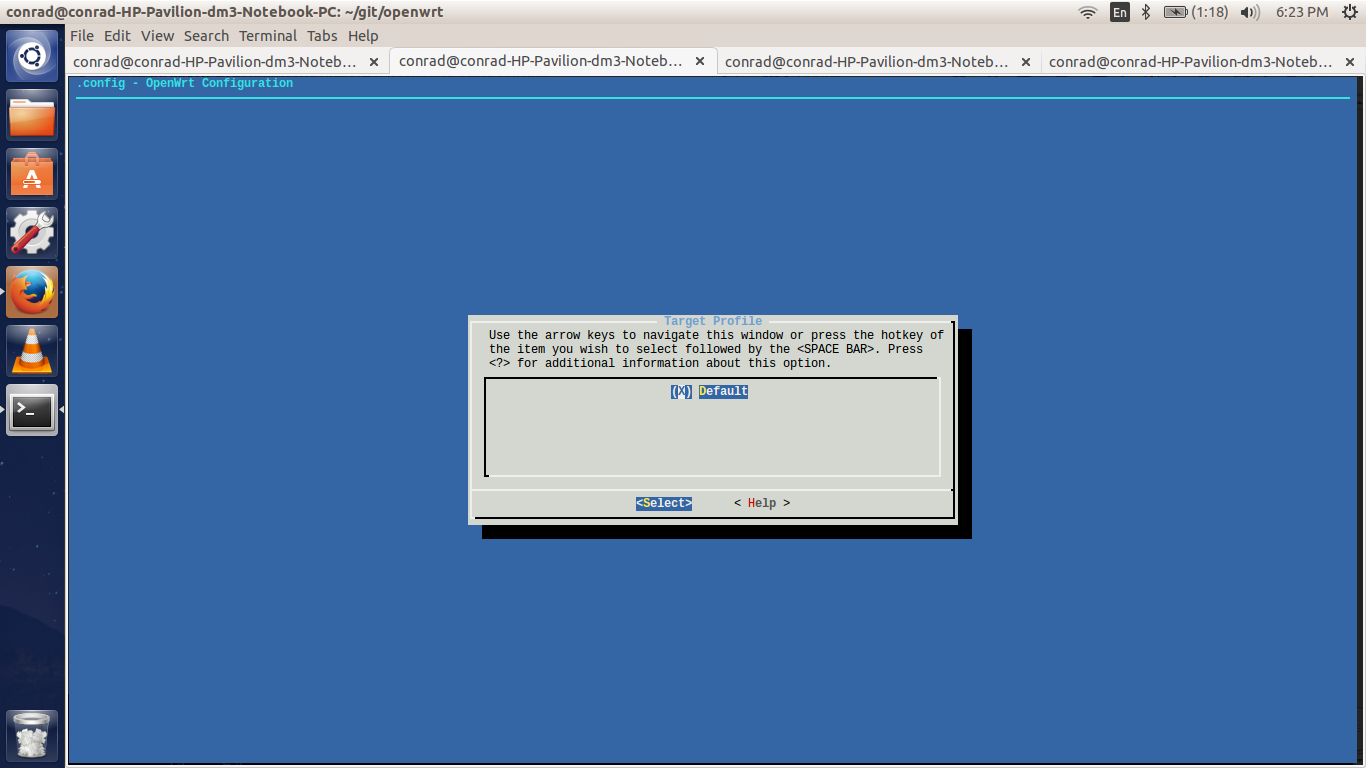
6.4. Selecting The Target Profile
Once the subtarget is selected we have to visit the "Target Profile" section and select an appropriate profile. If the target were set to "Lantiq" and subtarget were set to "XWAY" we would get the a couple of options as target profiles.
However in our setup the target is "MIPS Malta CoreLV (qemu)" and the subtarget is "Little Endian" and the only profile available is "Default".
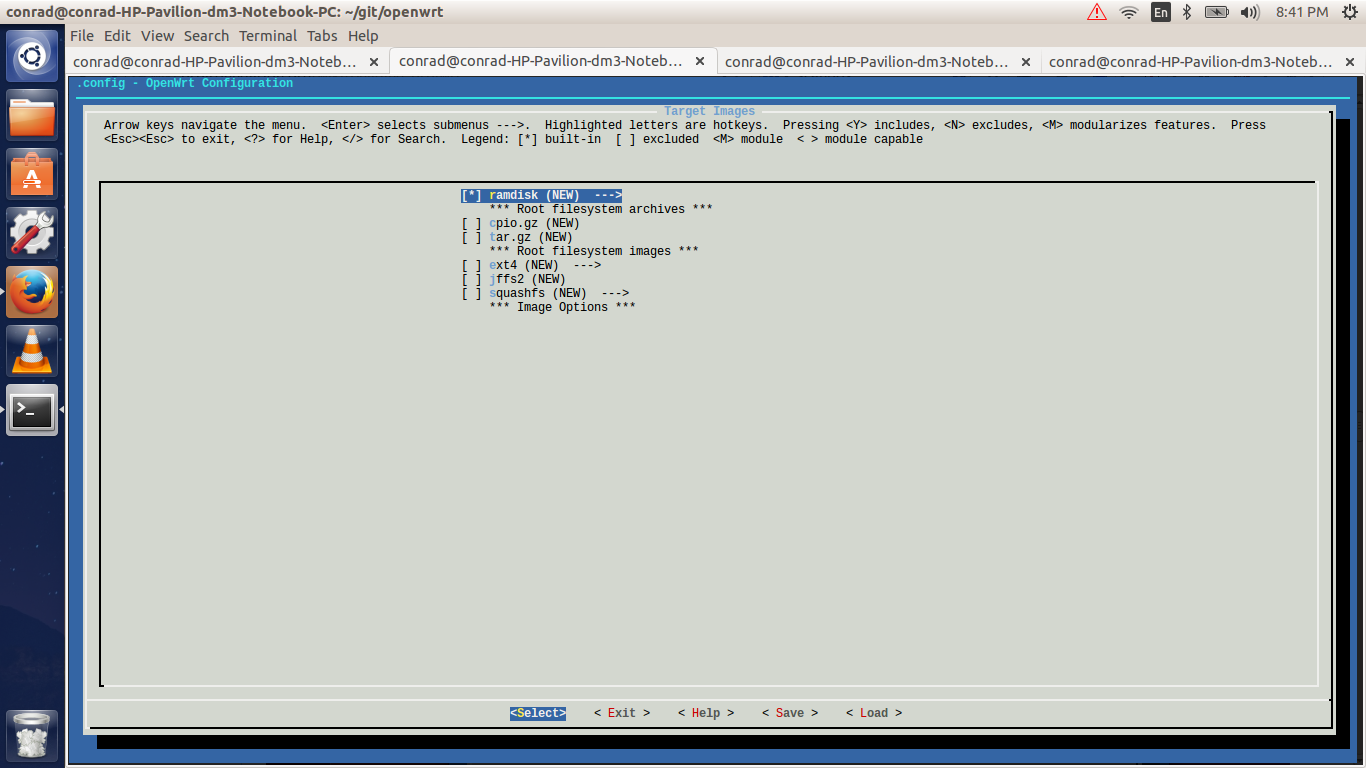
6.5. Selecting The Target Images
This option allows us to configure the way in which our system will boot. For our qemu system a ramdisk is sufficient. Select "ramdisk" in the target images submenu section. A ramdisk image is a compressed root file system image which is bundled along with the linux kernel. The kernel loads the ramdisk image into memory and starts the initialization scripts after mounting the root file system from the loaded ramdisk image.
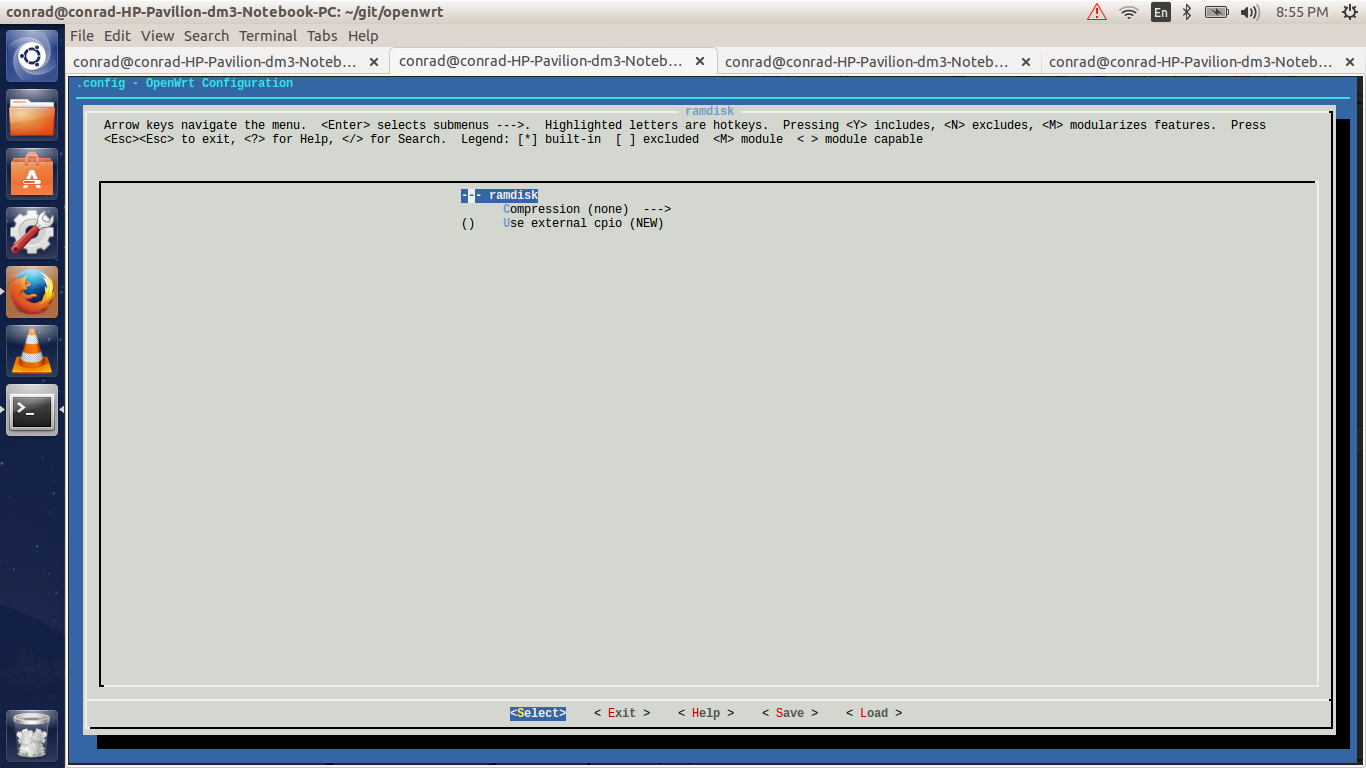
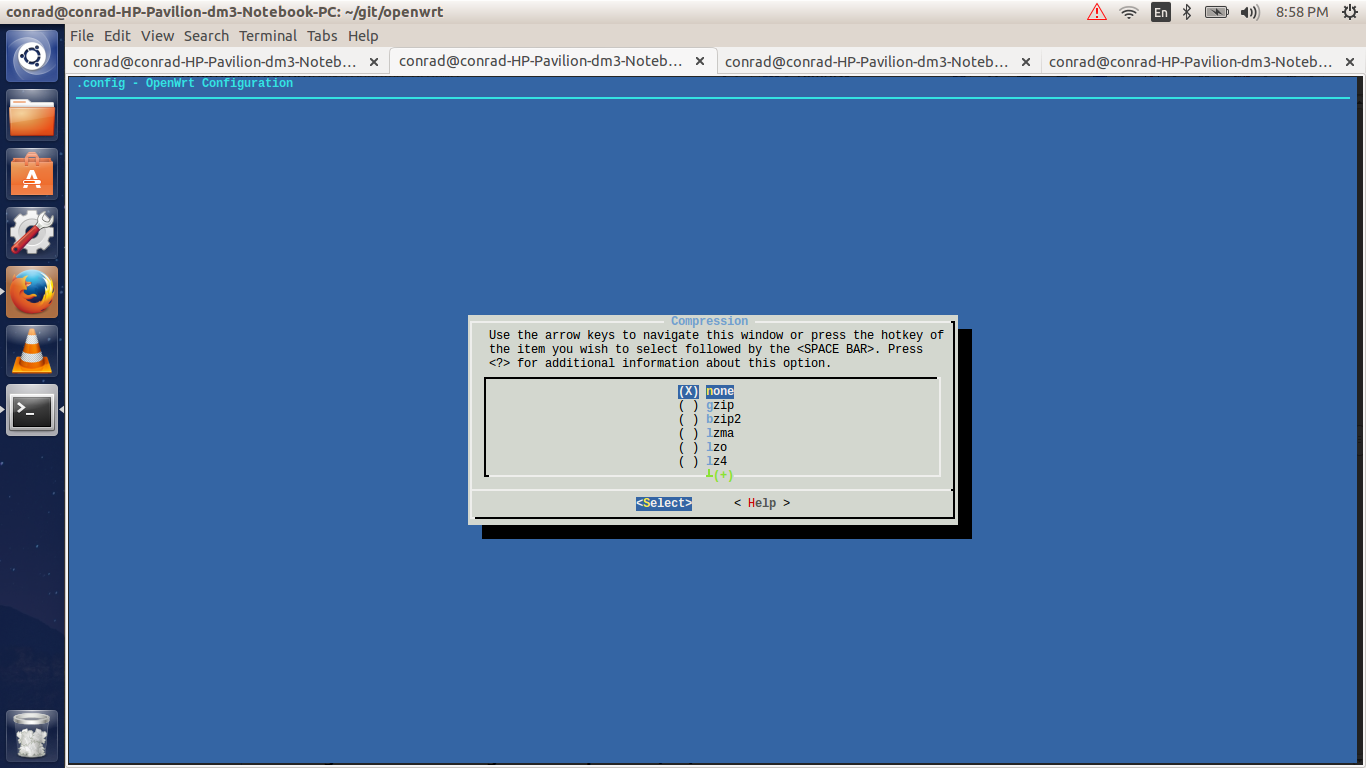
Hitting enter will select ramdisk from the submenu and will take us to a submenu for ramdisk which will allow us to configure the type of ramdisk. Below we see that the type of compression is set to none. This can be changed by selecting the compression option and choosing the type of compression desired.
The following is the list of compression types available. We keep the compression as none for now.
-
none
-
gzip
-
bzip2
-
lzma
-
lzo
-
lz4
-
xz
We will Exit all submenus as we don’t want to change the ramdisk settings.
6.6. Selecting Advanced Configuration Options
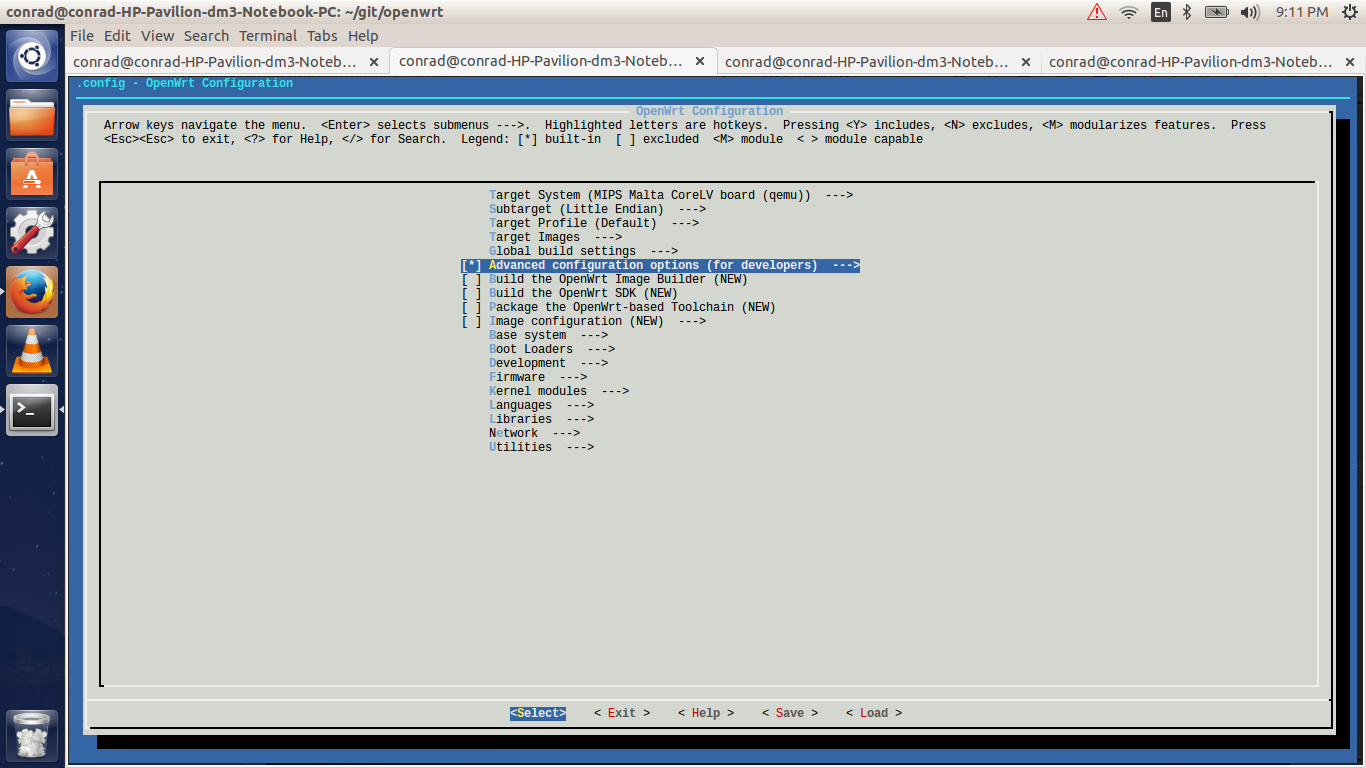
The advanced configuration options changes the build process of OpenWrt. This option is available in a checkbox and must first be selected before any configuration options can be made available. To do so after highlighting the advanced configuration options we have to hit the spacebar key. This will toggle the selection.
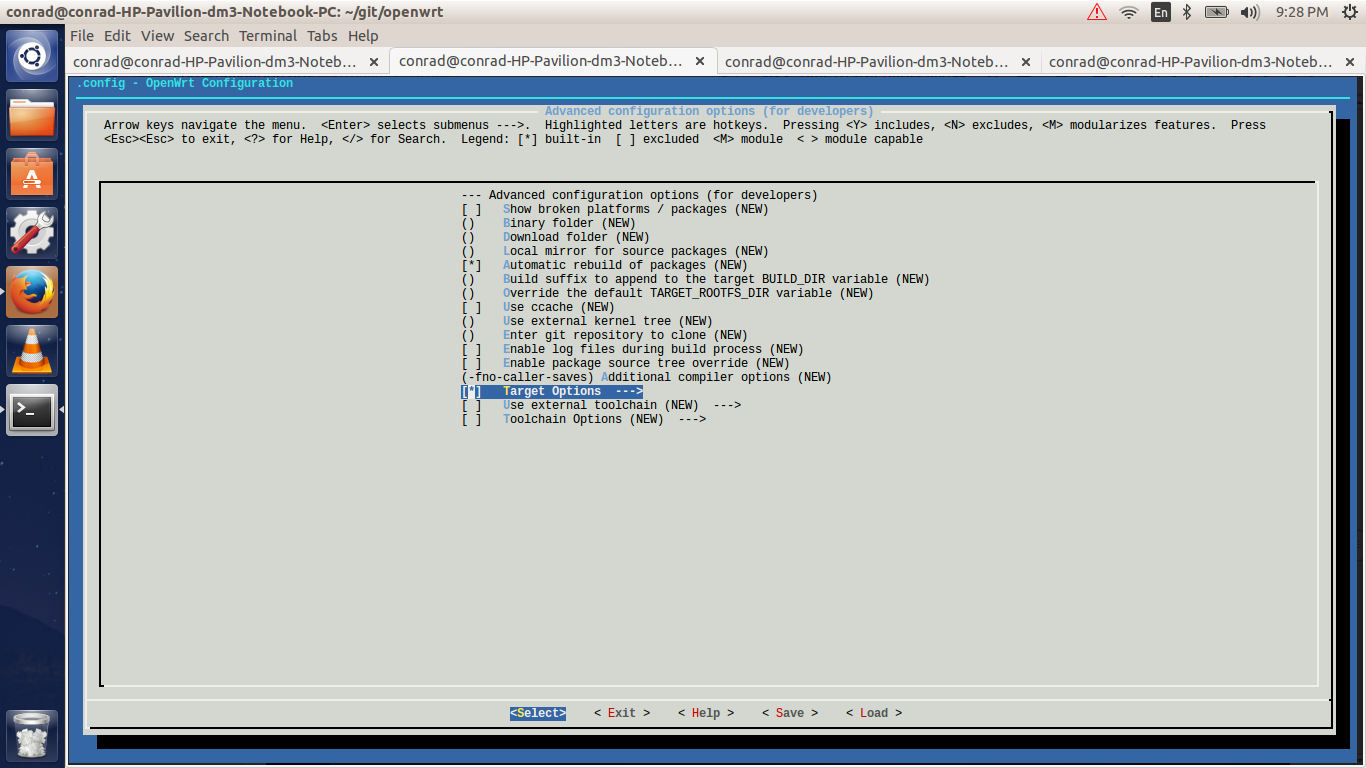
Next hit the enter key to open the submenu of the advanced configuration options. In our example we have to bypass a bug in the version of Qemu included as part of the Ubuntu 14.04 configuration. Go to the "Target Options" menu by pressing the down key and hit the spacebar key to select the item.
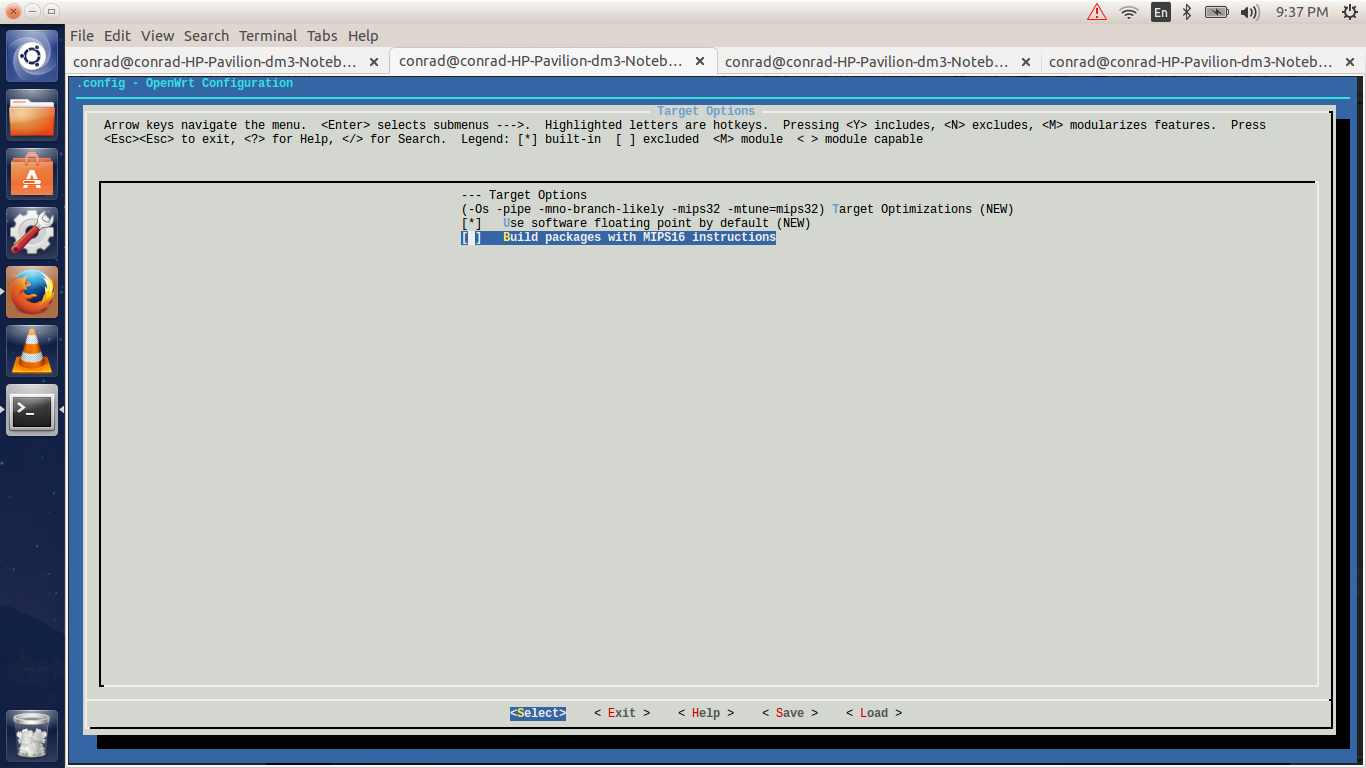
Hit the enter key to open the submenu of the target options. Go down and toggle the "Build packages with MIPS16 instructions" off.
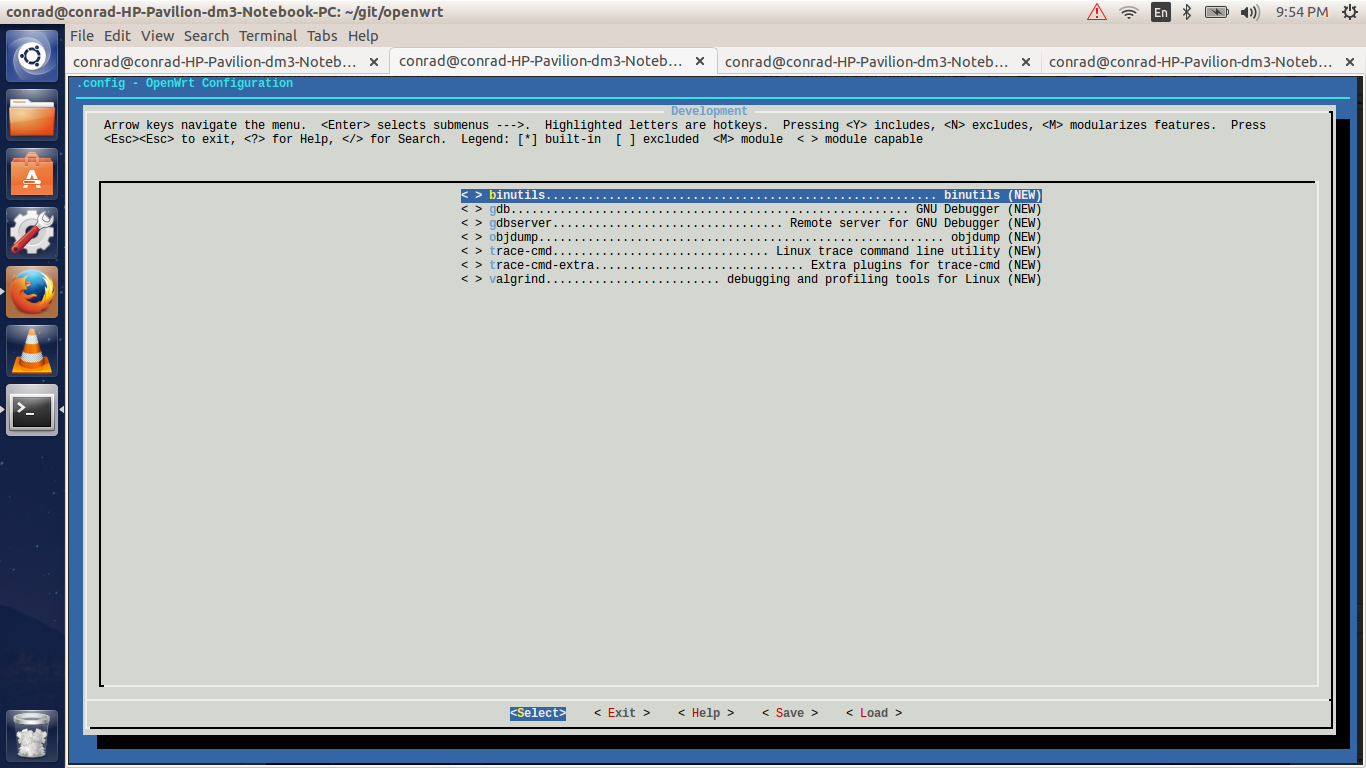
6.7. Selecting Included Software Packages
It is possible to select the software packages that included as part of the build of the image. We can select each of the following to see what gets built and packaged in the system.
-
Base Systems
-
Boot Loaders
-
Development
-
Firmware
-
Kernel modules
-
Languages
-
Libraries
-
Network
-
Utilities
For instance if we wanted to include debugging utilities like binutils or gdbserver we should select the Development option.
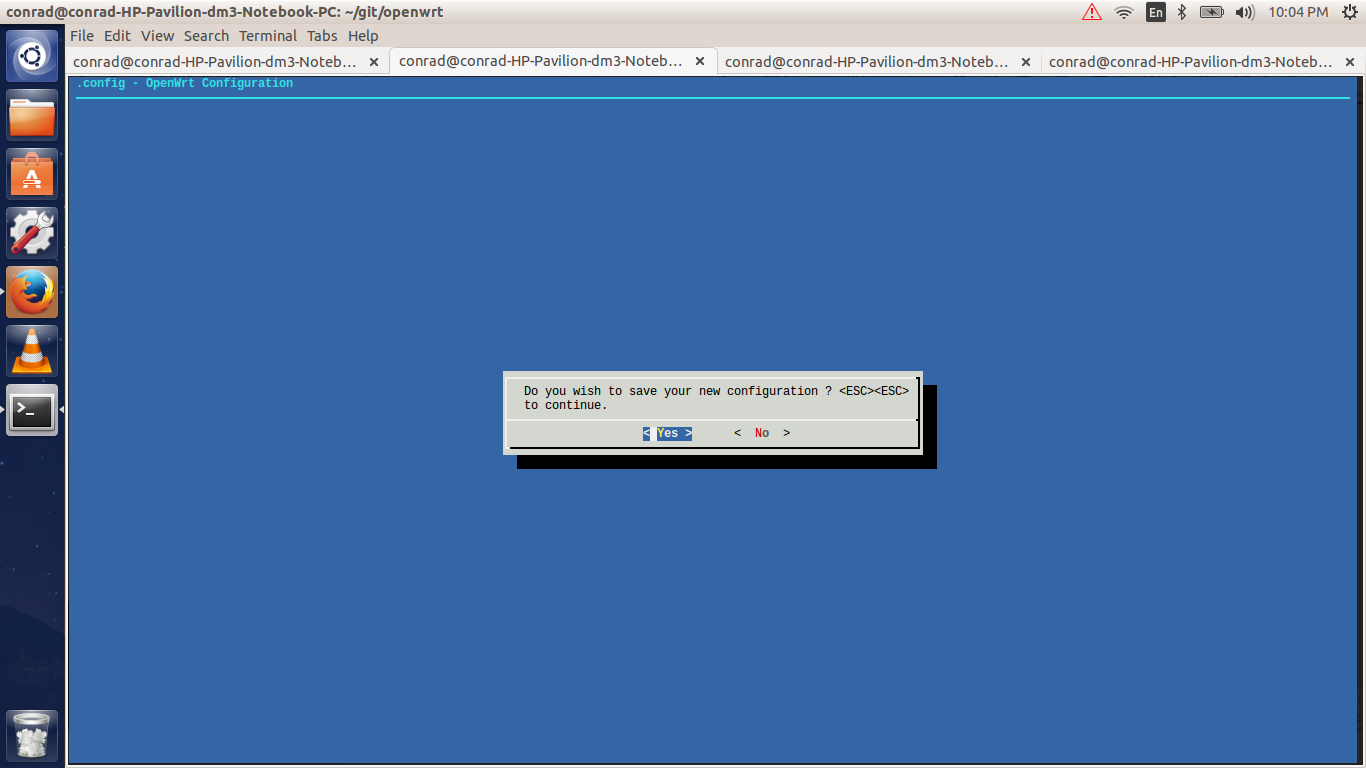
6.8. Saving The Configuration
After making all the changes required in the configuration setup we have to exit and savethe settings. This is done by simply navigating to the "Exit" option and hitting the enter key. We get a prompt asking if we want to save the new configuration.
By default the "Yes" option is selected and if we hit the enter key it saves the settings to a .config file. If we need to make additional changes we can hit the escape key to go back to the menuconfig. At the end after hitting the enter key and saving the configuration we get the following message on the terminal.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$ make menuconfig
configuration written to .config
*** End of the configuration.
*** Execute 'make' to start the build or try 'make help'.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$7. Building The Image
To build the image after configuration we have to run the make command. This short command kicks off a long duration build process. Make sure your workstation is connected to a power supply if you happend to be using a laptop.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$ make
make[1] world
make[2] tools/install
make[3] -C tools/patch compile
.
.
.After the build we can see how long it took by checking the timestamp of the bin/malta folder and the timestamp of the .config file. The build has taken roughly 2 hours and 40 minutes.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$ ls -l .config
-rw-rw-r-- 1 conrad conrad 80289 Nov 21 22:04 .config (1)
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$ ls -l bin/
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 3 conrad conrad 4096 Nov 22 00:40 malta (2)
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt$| 1 | Timestamp of .config is Nov 21 22:04 |
| 2 | Timestamp of the bin/malta folder is Nov 22 00:40 |
Let’s explore what is there in the bin directory.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$ ls -l
total 13020
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 262 Nov 22 09:19 md5sums
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 1634558 Nov 22 09:19 openwrt-malta-le-uImage-gzip
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 1171681 Nov 22 09:19 openwrt-malta-le-uImage-lzma
-rwxr-xr-x 1 conrad conrad 3456640 Nov 22 09:18 openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux.elf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 conrad conrad 7052928 Nov 22 09:19 openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf
drwxr-xr-x 3 conrad conrad 4096 Nov 22 00:03 packages
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$- md5sums
-
This gives the md5sum of the images built. There are four images built i.e. openwrt-malta-le-uImage-gzip, openwrt-malta-le-uImage-lzma, openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf and openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux.elf. The md5sums are useful for transferring the images between machines to ensure the images received are not corrupted or tampered with in anyway. It is always advisable to check the md5sum of your image with this file before using it.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$ cat md5sums
f31739d5ee3ce48489608e21d335ddb6 *openwrt-malta-le-uImage-gzip
5cad2704dc20f2dc35a277db0f8b65fe *openwrt-malta-le-uImage-lzma
b2c104f7d34f676e2b8d8e6d8a9d5e7d *openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf
3045acf878e5c22a4b4b3a96c85b2ad4 *openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux.elf
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$- openwrt-malta-le-uImage-gzip
-
This is a uboot kernel image compressed with gzip. We use the file command to describe the image information.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$ file openwrt-malta-le-uImage-gzip
openwrt-malta-le-uImage-gzip: u-boot legacy uImage, MIPS OpenWrt Linux-3.10.58, Linux/MIPS, OS Kernel Image (gzip), 1634494 bytes, Sat Nov 22 09:19:02 2014, Load Address: 0x80100000, Entry Point: 0x80104C50, Header CRC: 0xCCD1848F, Data CRC: 0x72F70CEC- openwrt-malta-le-uImage-lzma
-
This is a uboot kernel image compressed with lzma
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$ file openwrt-malta-le-uImage-lzma
openwrt-malta-le-uImage-lzma: u-boot legacy uImage, MIPS OpenWrt Linux-3.10.58, Linux/MIPS, OS Kernel Image (lzma), 1171617 bytes, Sat Nov 22 09:19:01 2014, Load Address: 0x80100000, Entry Point: 0x80104C50, Header CRC: 0xD7C70B9D, Data CRC: 0x8E08D874- openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf
-
This is a kernel image with the ramdisk root file system. The size of this file is the largest as it contains the application binaries and libraries in the system. It is an ELF executable.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$ file openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf
openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, MIPS, MIPS32 rel2 version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, stripped- openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux.elf
-
This is a kernel image as an ELF executable.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$ file openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux.elf
openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux.elf: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, MIPS, MIPS32 rel2 version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, stripped- packages
-
This contains the software packages in the form of IPK packages. The IPK package is the format of packaging used in OpenWrt to allow different packages to be installed in the system. Information about each of the packages is in the base/Packages file
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta/packages$ ls -lR
.:
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 2 conrad conrad 4096 Nov 22 09:17 base
./base:
total 1660
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 28432 Nov 22 00:11 base-files_156-r43202_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 230358 Nov 22 00:34 busybox_1.22.1-4_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 82572 Nov 22 00:29 dropbear_2014.65-2_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 17955 Nov 22 00:29 fstools_2014-10-27-d71297353dc45eaf8f7c252246490746708530f9_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 5183 Nov 22 00:13 hostapd-common_2014-10-25-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 43400 Nov 22 00:13 iw_3.15-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 6753 Nov 22 00:29 iwinfo_2014-10-27.1-d5dc3d0605f76fbbbad005d998497e53a236aeda_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 6331 Nov 22 00:04 jshn_2014-10-14-464e05e33b4c086be0bd932760a41ddcf9373187_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 8887 Nov 22 00:11 jsonfilter_2014-06-19-cdc760c58077f44fc40adbbe41e1556a67c1b9a9_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 816 Nov 22 00:11 kernel_3.10.58-1-bcf04f3a0c07d8943ddbeeaf32523287_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 111940 Nov 22 09:17 kmod-cfg80211_3.10.58+2014-10-08-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 850 Nov 22 00:11 kmod-crypto-aes_3.10.58-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 2035 Nov 22 00:11 kmod-crypto-arc4_3.10.58-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 7979 Nov 22 00:11 kmod-crypto-core_3.10.58-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 205609 Nov 22 09:17 kmod-mac80211_3.10.58+2014-10-08-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 17581 Nov 22 09:17 kmod-mac80211-hwsim_3.10.58+2014-10-08-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 829 Nov 22 00:11 kmod-mii_3.10.58-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 18144 Nov 22 00:11 kmod-pcnet32_3.10.58-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 4628 Nov 22 00:04 libblobmsg-json_2014-10-14-464e05e33b4c086be0bd932760a41ddcf9373187_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 218639 Nov 22 00:03 libc_0.9.33.2-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 32043 Nov 22 00:03 libgcc_4.8-linaro-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 23394 Nov 22 00:29 libiwinfo_2014-10-27.1-d5dc3d0605f76fbbbad005d998497e53a236aeda_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 13510 Nov 22 00:04 libjson-c_0.11-2_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 5906 Nov 22 00:04 libjson-script_2014-10-14-464e05e33b4c086be0bd932760a41ddcf9373187_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 13707 Nov 22 00:03 libnl-tiny_0.1-3_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 17511 Nov 22 00:04 libubox_2014-10-14-464e05e33b4c086be0bd932760a41ddcf9373187_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 9824 Nov 22 00:04 libubus_2014-09-17-4c4f35cf2230d70b9ddd87638ca911e8a563f2f3_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 16917 Nov 22 00:05 libuci_2014-04-11.1-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 12592 Nov 22 00:29 mtd_20_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 60241 Nov 22 00:05 netifd_2014-10-24-b46a8f3b9794efed197ffd2f6f62eb946de5f235_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 57377 Nov 22 00:32 opkg_9c97d5ecd795709c8584e972bfdf3aee3a5b846d-7_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 18108 Nov 22 09:19 Packages (1)
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 5350 Nov 22 09:19 Packages.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 35630 Nov 22 00:11 procd_2014-11-06-b899234bd657fa1ae1c71315326c3fe2cd9b6cec_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 24433 Nov 22 00:06 ubox_2014-10-06-0b274c16a3f9d235735a4b84215071e1e004caa9_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 5027 Nov 22 00:04 ubus_2014-09-17-4c4f35cf2230d70b9ddd87638ca911e8a563f2f3_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 8626 Nov 22 00:04 ubusd_2014-09-17-4c4f35cf2230d70b9ddd87638ca911e8a563f2f3_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 7718 Nov 22 00:05 uci_2014-04-11.1-1_malta_mipsel.ipk
-rw-r--r-- 1 conrad conrad 220488 Nov 22 00:13 wpad-mini_2014-10-25-1_malta_mipsel.ipk| 1 | Information about all the packages built is present in this file. |
8. Booting The Image
All the built images and packages are in the bin/malta directory. We will now boot the openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf image file with qemu in little endian mode. The -nographic option instructs QEMU to turn off all graphic output and send all command lne output and input to the terminal. The -kernel option instructs QEMU to boot the following image file.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/git/openwrt/bin/malta$ qemu-system-mipsel -kernel openwrt-malta-le-vmlinux-initramfs.elf -nographic
qemu-system-mipsel: pci_add_option_rom: failed to find romfile "efi-pcnet.rom"
qemu-system-mipsel: pci_add_option_rom: failed to find romfile "vgabios-cirrus.bin"
[ 0.000000] Linux version 3.10.58 (conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC) (gcc version 4.8.3 (OpenWrt/Linaro GCC 4.8-2014.04 r43202) ) #4 SMP Sat Nov 22 09:18:49 IST 2014
[ 0.000000] Config serial console: console=ttyS0,38400n8r
[ 0.000000] bootconsole [early0] enabled
[ 0.000000] CPU revision is: 00019300 (MIPS 24Kc)
[ 0.000000] FPU revision is: 00739300
[ 0.000000] Software DMA cache coherency enabled
.
.
.
_______ ________ __
| |.-----.-----.-----.| | | |.----.| |_
| - || _ | -__| || | | || _|| _|
|_______|| __|_____|__|__||________||__| |____|
|__| W I R E L E S S F R E E D O M
-----------------------------------------------------
CHAOS CALMER (Bleeding Edge, r43202)
-----------------------------------------------------
* 1 1/2 oz Gin Shake with a glassful
* 1/4 oz Triple Sec of broken ice and pour
* 3/4 oz Lime Juice unstrained into a goblet.
* 1 1/2 oz Orange Juice
* 1 tsp. Grenadine Syrup
-----------------------------------------------------
root@OpenWrt:/#