Benchmarking RT Preempt Kernel 3.18 On BeagleBone Black
by Conrad Gomes on
In this post we will run the cyclictest utility and benchmark the RT Preempt Kernel on BeagleBone Black We need to check the realtime performance of the RT Preempt kernel against the vanilla kernel. To do this we will run the cyclictest utility and measure the performance.
Clone The rt-tests Sources
First clone the source code
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git$ git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/clrkwllms/rt-tests.git
Cloning into 'rt-tests'...
remote: Counting objects: 2830, done.
remote: Total 2830 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (2830/2830), 512.57 KiB | 164.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (1692/1692), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git$Cross-Compiling The rt-tests Sources
Cross-compile the rt-tests by passing the CC as arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc.
|
Do not use CROSS_COMPILE
The cyclictest wiki states that CROSS_COMPILE is to be used in order to cross-compile the sources. However this is not honored by the Makefile and will lead to a build of x86 binaries instead of ARM binaries. Use CC instead and it should work. |
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git/rt-tests$ make CC=arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc clean (1)
for F in cyclictest pi_stress pip_stress pmqtest rt-migrate-test signaltest ptsematest sigwaittest svsematest sendme hackbench *.o .depend *.*~ *.orig *.rej rt-tests.spec *.d *.a ChangeLog; do find -type f -name $F | xargs rm -f; done
rm -f hwlatdetect
rm -f tags
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git/rt-tests$
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git/rt-tests$ make CC=arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc all (2)
arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc -D VERSION_STRING=0.91 -c src/cyclictest/cyclictest.c -Wall -Wno-nonnull -O2 -D_GNU_SOURCE -Isrc/include
In file included from src/cyclictest/cyclictest.c:39:0:
src/cyclictest/rt_numa.h: In function ‘numa_on_and_available’:
src/cyclictest/rt_numa.h:259:2: warning: implicit declaration of function ‘numa_available’ [-Wimplicit-function-declaration]
src/cyclictest/cyclictest.c: In function ‘tracemark’:
src/cyclictest/cyclictest.c:433:7: warning: ignoring return value of ‘write’, declared with attribute warn_unused_result [-Wunused-result]
src/cyclictest/cyclictest.c: In function ‘tracing’:
src/cyclictest/cyclictest.c:446:9: warning: ignoring return value of ‘write’, declared with attribute warn_unused_result [-Wunused-result]
src/cyclictest/cyclictest.c:456:9: warning: ignoring return value of ‘write’, declared with attribute warn_unused_result [-Wunused-result]
arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc -D VERSION_STRING=0.91 -c src/lib/rt-utils.c -Wall -Wno-nonnull -O2 -D_GNU_SOURCE -Isrc/include
arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc -D VERSION_STRING=0.91 -c src/lib/error.c -Wall -Wno-nonnull -O2 -D_GNU_SOURCE -Isrc/include
arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc -D VERSION_STRING=0.91 -c src/lib/rt-get_cpu.c -Wall -Wno-nonnull -O2 -D_GNU_SOURCE -Isrc/include
arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc -D VERSION_STRING=0.91 -c src/lib/rt-sched.c -Wall -Wno-nonnull -O2 -D_GNU_SOURCE -Isrc/include
ar rcs librttest.a rt-utils.o error.o rt-get_cpu.o rt-sched.o
arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc -Wall -Wno-nonnull -O2 -o cyclictest cyclictest.o librttest.a -lrt -lpthread -lrttest -L.
.
.
.
ln -s src/hwlatdetect/hwlatdetect.py hwlatdetect
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git/rt-tests$
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git/rt-tests$ file cyclictest (3)
cyclictest: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, EABI5 version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=f849bb56948e70e80282318453629a15d4eb4844, not stripped
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git/rt-tests$
conrad@conrad-HP-Pavilion-dm3-Notebook-PC:~/Git/rt-tests$ cp cyclictest ~/fe-kernel-training/linux-kernel-labs/modules/nfsroot/bin/. (4)| 1 | Cleaning the source code |
| 2 | Cross-compiling all |
| 3 | The file command shows it has been cross-compiled |
| 4 | Copy the cyclictest to the NFS root filesystem folder |
Finally we boot up the board and test if we’re able to print the version of cyclictest with the "-h" option.
# cyclictest --help
cyclictest V 0.91 (1)
Usage:
cyclictest <options>
.
.
.| 1 | Version is 0.91 |
Different Configurations Of The Kernel
We will be evaluating for different versions of the RT Preempt 3.18 kernel
for BeagleBone Black. The instructions to port RT Preempt to the BeagleBone
Black kernel are given in the following posts:
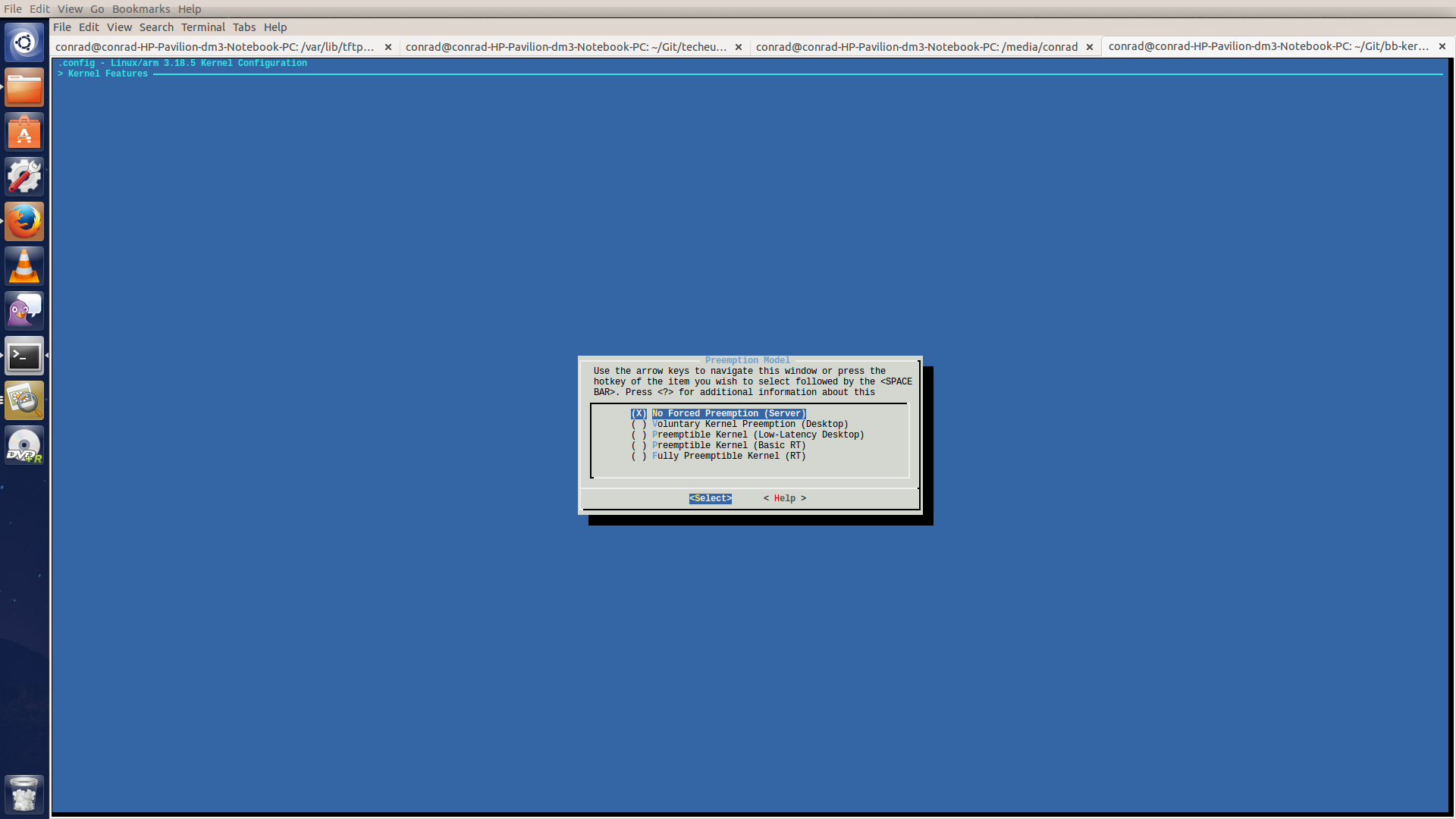
We create four different builds with different preemption configuraitons to compare the real-time behavior of the kernels. To change the configuration we go to Kernel Features --→ Preemption Model and select the type of preemption required.
Torturing The Kernel
We’ll follow the steps given in the following link to benchmark the various kernels:
http://erlerobotics.gitbooks.io/erle-robotics-erle-brain-a-linux-brain-for-drones/content/en/software/kernel.html
First we run stress in the background to spawn 64 CPU intensive tasks, 64 input/ouput tasks and 2 tasks spinning on malloc/free.
# stress --cpu 64 --io 64 --vm 2 --vm-bytes 128M &
# stress: info: [220] dispatching hogs: 64 cpu, 64 io, 2 vm, 0 hdd (1)
#
# ps
PID USER COMMAND
1 root init
2 root [kthreadd]
3 root [ksoftirqd/0]
.
.
.
220 root stress --cpu 64 --io 64 --vm 2 --vm-bytes 128M (2)
221 root stress --cpu 64 --io 64 --vm 2 --vm-bytes 128M
.
.
.
351 root ps
#| 1 | Running stress |
| 2 | The tasks spawned by stress are listed using the ps command |
The load gradually increases and we wait until it is greater than 100 as shown below. We use uptime to measure the load on the system. It gives the system load averages for the past 1, 5 and 15 minutes.
System load averages is the average number of processes that are either in a runnable or uninterruptable state. A process in a runnable state is either using the CPU or waiting to use the CPU. A process in uninterruptable state is waiting for some I/O access, eg waiting for disk.
# uptime
00:52:19 up 45 min, load average: 28.94, 6.42, 2.44
# uptime
00:52:24 up 45 min, load average: 37.03, 8.47, 3.12
# uptime
00:52:26 up 45 min, load average: 37.03, 8.47, 3.12
# uptime
00:52:28 up 45 min, load average: 44.55, 10.51, 3.81
# uptime
00:52:30 up 45 min, load average: 44.55, 10.51, 3.81
# uptime
00:52:41 up 46 min, load average: 57.69, 14.44, 5.16
#
# uptime
00:56:54 up 50 min, load average: 128.98, 80.81, 35.15 (1)
# uptime
01:03:24 up 56 min, load average: 130.07, 116.68, 67.69 (2)
#| 1 | The load crosses 128 which indicates that on average the 130(64 + 64 + 2) tasks are created |
| 2 | The load after 3 minutes has increased to ~130 and the 5 minute load has also increased to 67.69 |
Running cyclictest
After the system has been "stressed" out we can run the cyclictest to measure the latencies(us). This will give us the realtime performance of the kernels. We will now compare the results of the different kernels.
No Forced Preemption
- Min
-
15 us
- Avg
-
36 us
- Max
-
2235 us
# cyclictest -t1 -p 80 -n -i 10000 -l 10000
# /dev/cpu_dma_latency set to 0us
policy: fifo: loadavg: 130.62 100.00 48.77 131/180 279
T: 0 ( 283) P:80 I:10000 C: 10000 Min: 15 Act: 31 Avg: 36 Max: 2235
#Preemptible Low Latency Kernel
- Min
-
19 us
- Avg
-
32 us
- Max
-
233 us
# cyclictest -t1 -p 80 -n -i 10000 -l 10000
# /dev/cpu_dma_latency set to 0us
policy: fifo: loadavg: 130.61 95.66 45.16 131/186 248
T: 0 ( 247) P:80 I:10000 C: 10000 Min: 19 Act: 32 Avg: 32 Max: 233
#Summary Of Tests
We see that the minimum, average and maximum latencies are lowest for the fully preemptible RT Kernel.
| Kernel Type | Min (us) | Avg (us) | Max(us) |
|---|---|---|---|
No Forced Preemption |
15 |
36 |
2235 |
Preemptible Low Latency Kernel |
19 |
32 |
233 |
Preemptible Basic RT Kernel |
19 |
34 |
183 |
Fully Preemptible RT Kernel |
14 |
26 |
43 |
The compiled kernels, configuration files, generated device tree binaries, modules and firmware are available here.